Hydrogen is an important energy carrier and chemical feedstock. It is currently mainly produced from fossil fuels, resulting in close to 900 million tonnes of GHG emissions per year.
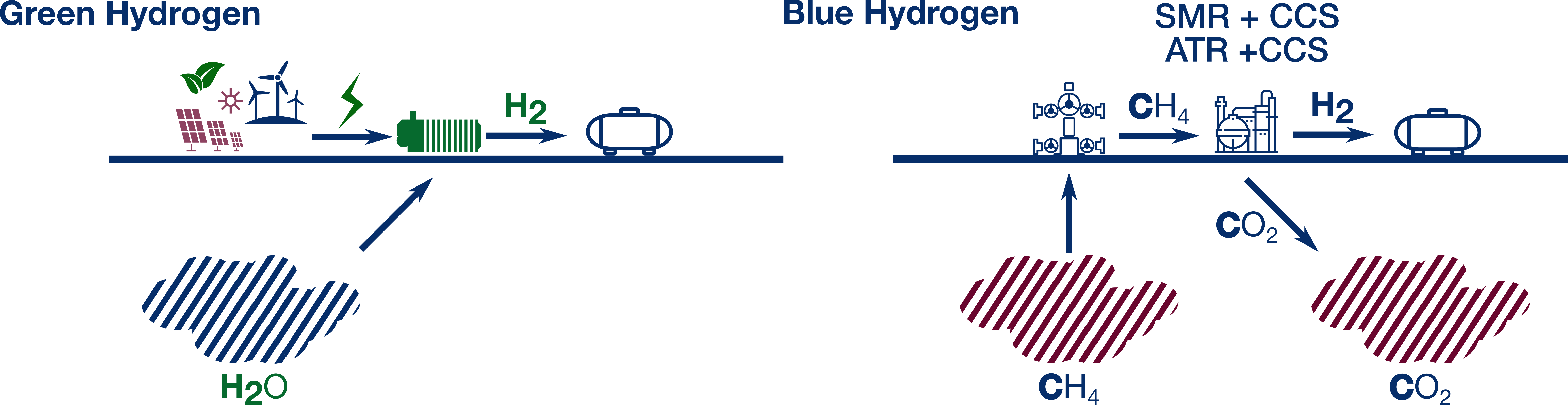
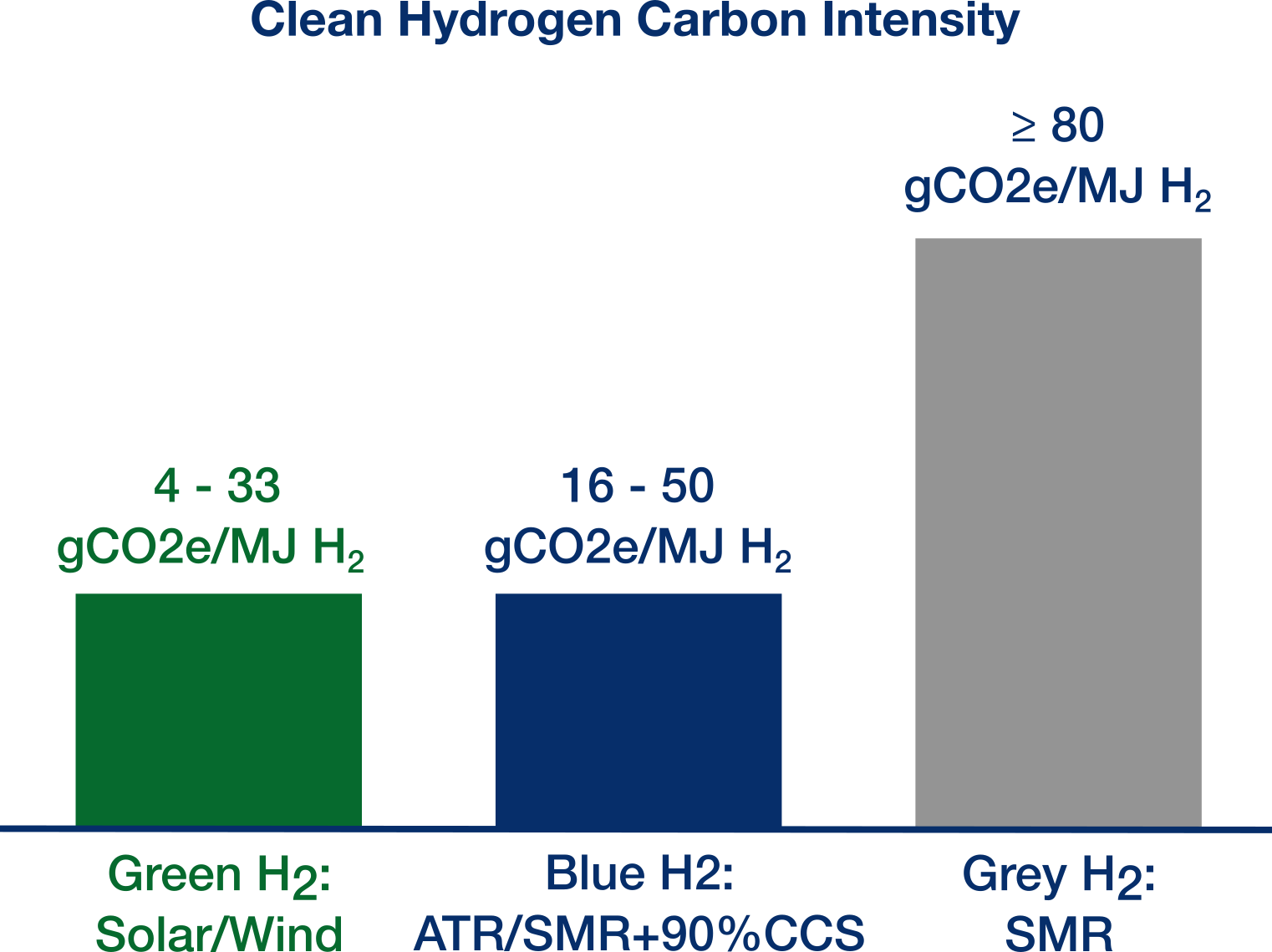
Low-emissions Clean Hydrogen can be produced from natural gas with carbon capture (Blue Hydrogen), or from water by using electrolysis and renewable electricity (Green Hydrogen).
Hydrogen provides clean energy with no point source carbon emissions, making it an excellent choice for decarbonizing hard-to-electrify sectors. Quantiam has developed catalysts which greatly increase the efficiency and reduce the cost of producing Green Hydrogen via alklaine water electrolysis (AWE).
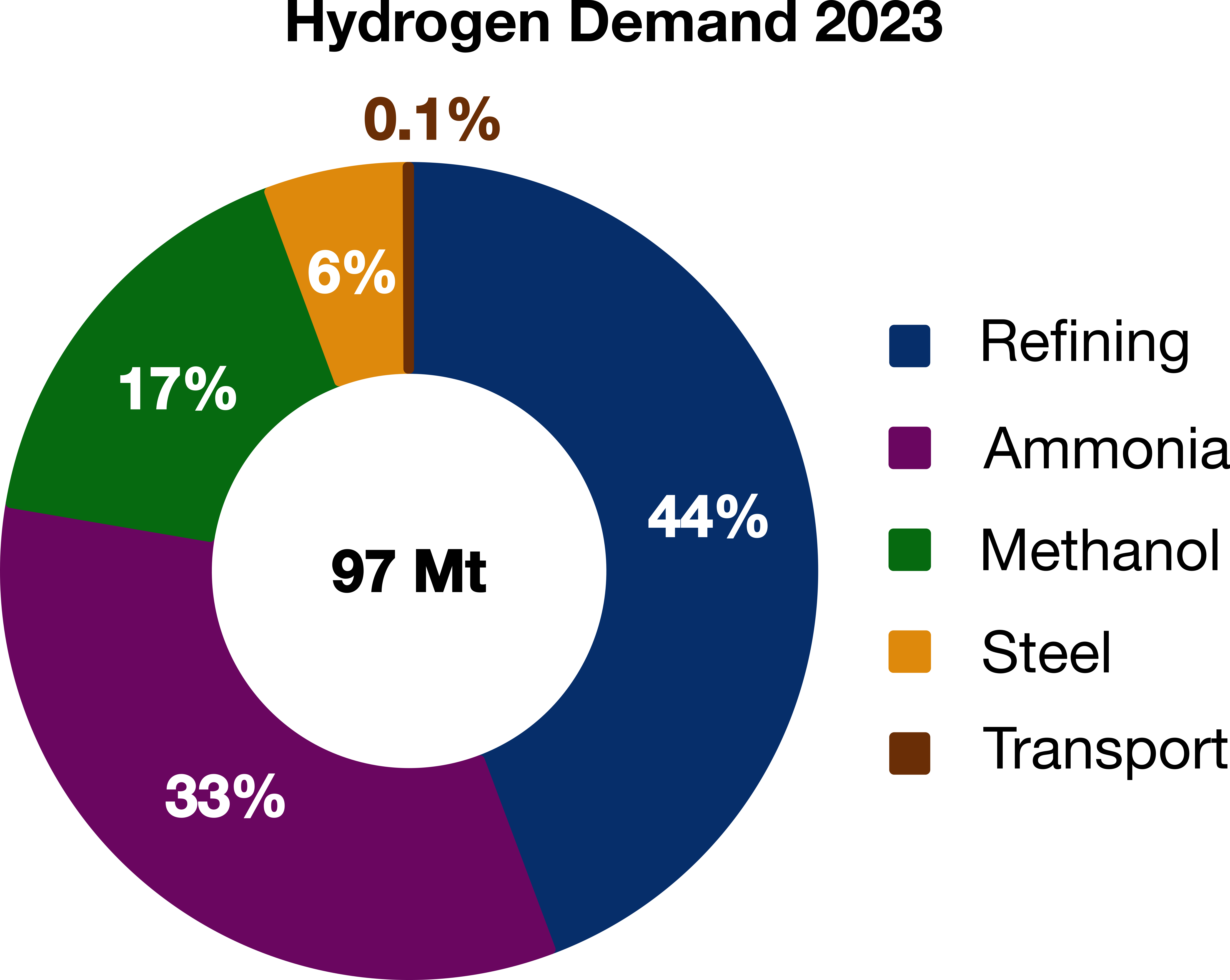
In 2023, global hydrogen demand reached a new high of more than 97 million metric tonnes, and it is expected to grow to over 300 million metric tonnes by 2050. By 2030, Clean Hydrogen production is expected to account for almost half of hydrogen demand, according to the International Energy Agency.
Quantiam has developed world-class catalytic coatings for the anodes and cathodes used in alkaline water electrolysis (AWE) stacks. Quantiam's catalysts greatly increase electrolyzer operation and performance enabling cost-effective Green Hydrogen production at scale.
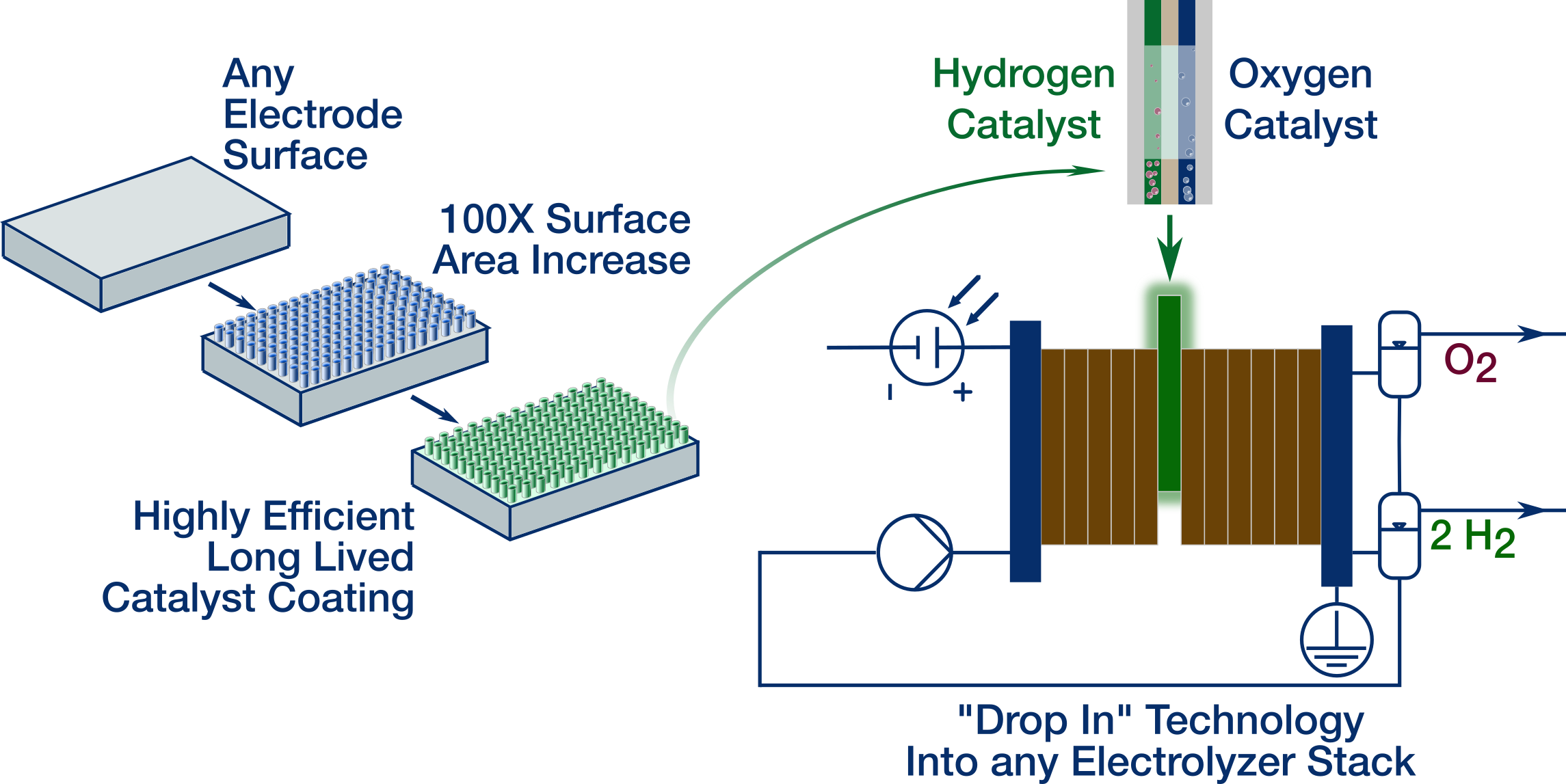
Quantiam’s high surface area catalysts reduce the energy input required to split water into Hydrogen and Oxygen to nearly the limit set by nature.
Quantiam’s catalysts show minimal degradation with projected stack lifetimes of at least 7-10 years.
Our proprietary catalysts can be coated onto any electrode enabling easy drop-in installation into any electrolyzer stack design.
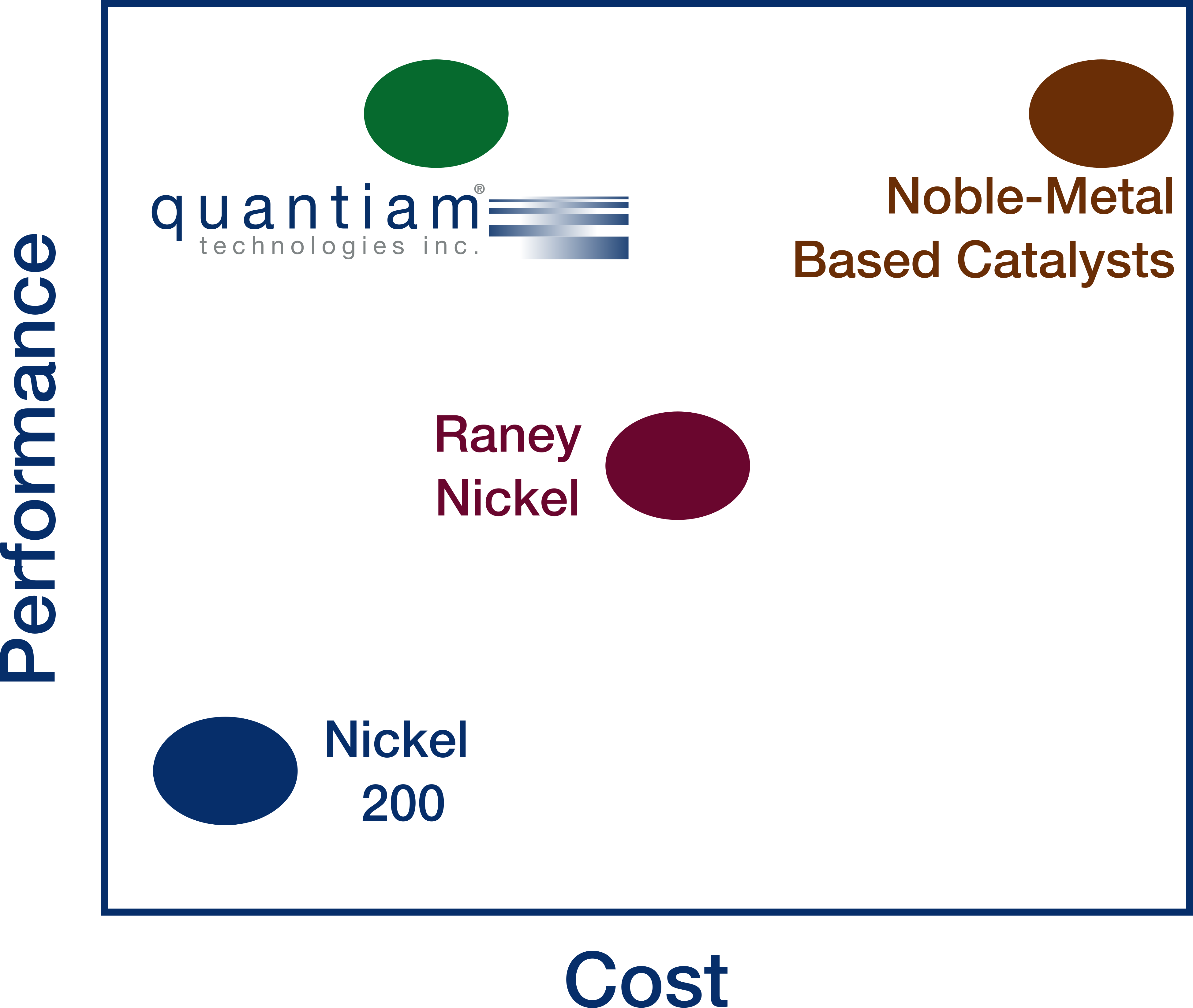
Quantiam's alkaline water electrolysis (AWE) catalysts use earth abundant, supply chain risk-free materials, offering the performance of typical noble-metal catalysts at a fraction of the cost.
Want to learn more about our solutions to maximize the performance of your electrolyzer stacks?